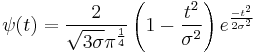Mexican hat wavelet
In mathematics and numerical analysis, the Mexican hat wavelet
is the negative normalized second derivative of a Gaussian function, i.e., up to scale and normalization, the second Hermite function. It is a special case of the family of continuous wavelets (wavelets used in a continuous wavelet transform) known as Hermitian wavelets. It is usually only referred to as the "Mexican hat" in the Americas, due to cultural association; see "sombrero". In technical nomenclature this function is known as the Ricker wavelet, where it is frequently employed to model seismic data.
The multidimensional generalization of this wavelet is called the Laplacian of Gaussian function. In practice, this wavelet is sometimes approximated by the difference of Gaussians function, because it is separable and can therefore save considerable computation time in two or more dimensions. The scale normalised Laplacian (in 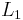 -norm) is frequently used as a blob detector and for automatic scale selection in computer vision applications; see Laplacian of Gaussian and scale-space. The Mexican hat wavelet can also be approximated by derivatives of Cardinal B-Splines[1]
-norm) is frequently used as a blob detector and for automatic scale selection in computer vision applications; see Laplacian of Gaussian and scale-space. The Mexican hat wavelet can also be approximated by derivatives of Cardinal B-Splines[1]
References
- ^ Brinks R: On the convergence of derivatives of B-splines to derivatives of the Gaussian function, Comp. Appl. Math., 27, 1, 2008